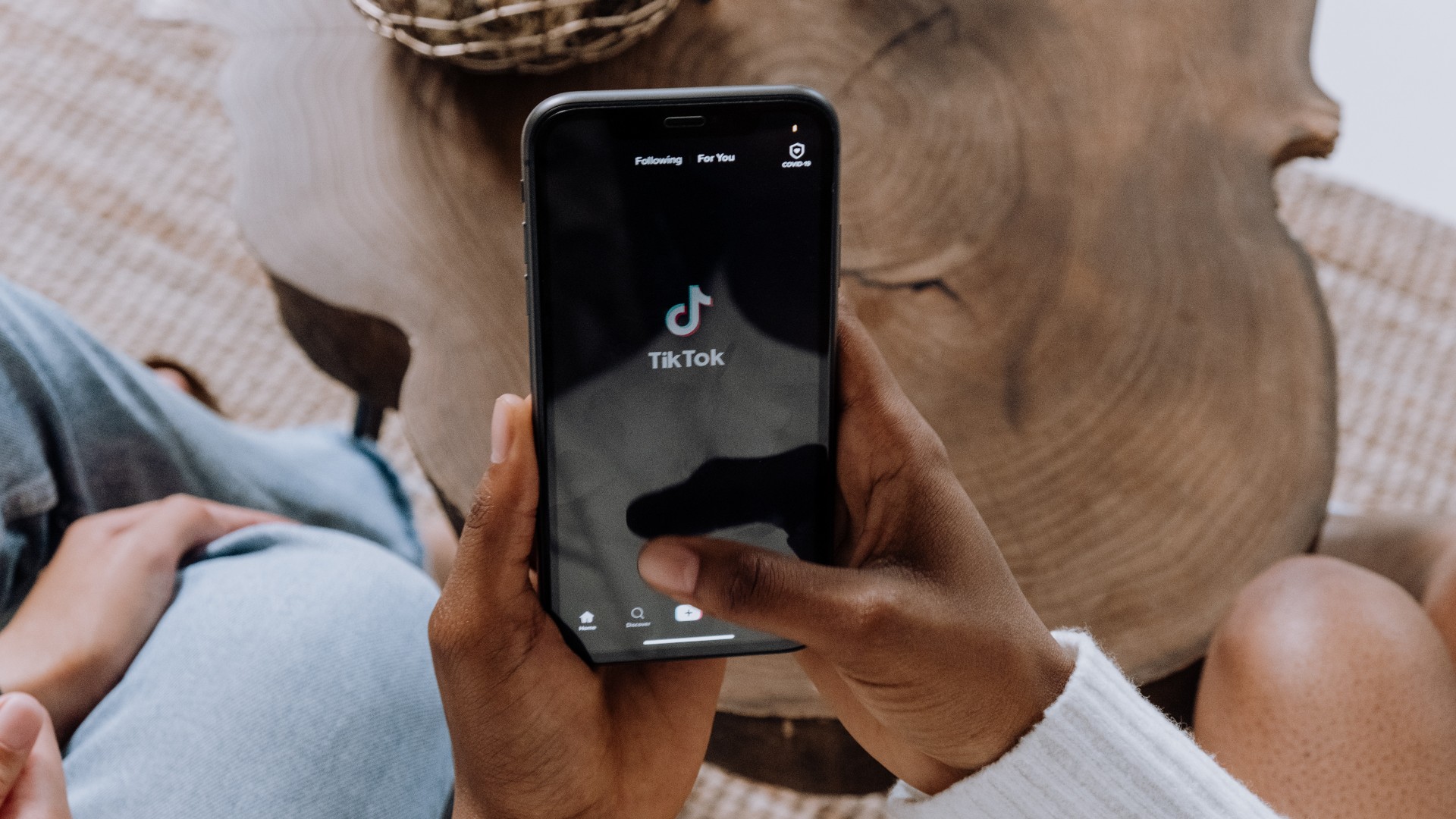
TikTok is failing to protect young users
Sparking fresh concerns about the platform’s influence on children, new research has uncovered that its algorithm is pushing videos about eating disorders and self-harm to 13-year-olds. According to research from the Centre for Countering Digital Hate (CCDH), TikTok appears to be pushing videos about eating disorders and self-harm to...
Current in News
NASA says astronauts will be living on moon by 2030
Think inhabiting the moon is stuff of science fiction fantasy? One NASA official reckons it will be a reality by the end of this decade, with the latest Artemis 1 mission the ‘first step.’ Astronauts could be living and working on the moon by 2030, one NASA official says. Head of...
Scientists have made a huge nuclear fusion breakthrough
In the quest to unlock a ‘near-limitless, safe, clean’ source of energy, researchers in the US have reportedly succeeded in sparking a fusion reaction that created more energy than it consumed. According to the Financial Times, US government scientists have made a breakthrough in the pursuit of limitless, zero-carbon...
Cryptocurrency Zilliqa is launching a Web3 gaming console in 2023
Popular cryptocurrency Zilliqa is launching its own Web3 games console for 2023. It will reportedly allow players to earn coins while playing its exclusive titles. Does this model have the potential to take off within the industry? While we hear constant talk of the impending Metaverse, Web3 isn’t discussed nearly...
Nicole Mann becomes first Indigenous woman in space
Mann – a NASA astronaut – has become the first Native American to travel into space. Last Wednesday NASA launched its SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule to the International Space Station. On board were a team of NASA crewmates; Anna Kikina, Josh Cassada, and Koichi Wakata. Their commander was Nicole Aunapu Mann...
Why Kim won’t be the one suffering for her crypto touting
Despite paying the SEC $1.26 million for an undisclosed Instagram ad, Kim Kardashian’s hefty fine is nothing compared to the impacts on those she scammed. Kim Kardashian has been forced to pay $1.2 million to the Securities and Exchange Commission for an undisclosed promotion of EMAX tokens, a crypto asset...
South African teenagers build solar-powered train
Amid South Africa’s power cuts, a group of students built the country’s first fully solar-powered train. The power outages have caused disruptions affecting poor and working-class commuters relying on trains. A group of 20 South African students from Soshanguve Technical School recently showcased a fully solar-powered train at a university event. The prototype, which has taken approximately two years to build, is set to redefine railway travel not only in...
Google finally shuts down game streaming service Stadia
The cloud-based gaming dream is finally dead for Google, as it announces a shutdown of all Stadia services and features. The platform will officially retire in January 2023. Remember when Stadia was touted as the next step for video games? Google’s experimental tread into gaming showed promise. Using cloud-based streaming, it teased a world where players could jump into Red Dead Redemption 2 on their iPhone or load up Cyberpunk...
YouTube reports Gen Z want curated content over viral videos
It seems the days of dancing foxes, Gangnam Style, and other viral content are over. New studies suggest that Gen Z prefer to see specific, tailored content for them, rather than popular videos intended for all audiences. If you’re an older Gen Zer like myself, you may remember a time when viral content was everywhere. Whether it was dancing foxes, novelty songs, talking unicorns, or anything in between, widespread, short-form...
Perseverance Mars rover discovers abundance of organic molecules
NASA says its Perseverance rover is finding organic molecules on ‘every target’ that it observes, providing further evidence to suggest that Mars was once teeming with life. New data from NASA’s rover, Perseverance, has reinforced suggestions that life may have existed on Mars billions of years ago. A press conference was held last Thursday to showcase the findings. Perseverance has discovered a variety of organic modules in Jezero Crater, an ancient lake...