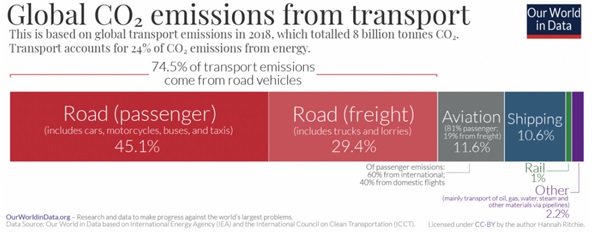
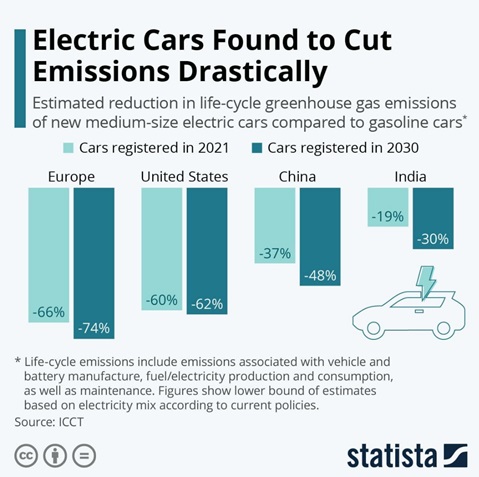
Considering the vital role of the auto industry in certain economies and the fact that urban planning seems to almost centre on making space for cars, it makes sense that electrifying vehicles is the preferred transport solution for many countries.
However, such a solution is not entirely feasible for every city or country.
Rather than having consumers take on the cost of purchasing an electric vehicle, some believe we should focus on intelligent urban design that prioritises pedestrians and cyclists (the lowest emitting forms of transportation) over cars.
For example, “complete neighbourhoods” allow most residents to access their basic needs by either foot or bike. Roads would mainly be used for public transit, moving goods from place to place, and emergency services.
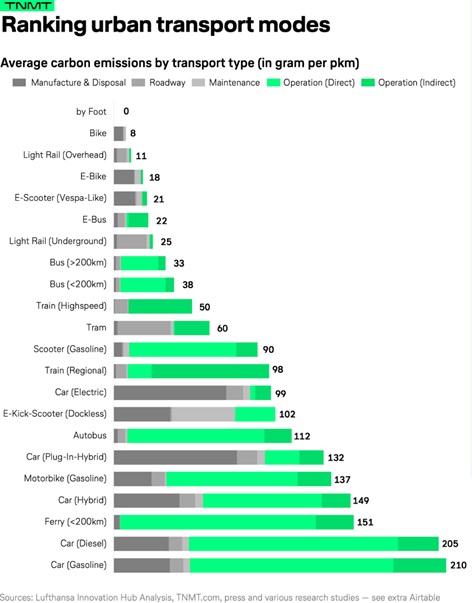
But electrification and improvements to urban planning and public transit need to be implemented in unison. Ideally, the world will eventually transition away from cars and toward affordable, accessible and electric public transit.
What is COP26 doing about it?
Many cities are moving in the right direction with prioritising improvements to public transit and city planning.
Still, such has not seemed to be the focus of COP26 when it comes to transport. The COP26 Declaration on Accelerating the Transition to 100% Zero Emissions Cars and Vans has been at the heart of discussions on transportation.
Through said Declaration, over 20 countries and 6 major vehicle manufacturers have set out for all new car and van sales to be zero emissions by 2040 globally. Other countries have also made commitments to deploying charging infrastructure for EVs, improving fuel efficiency standards and more.
But as the COP26 Transport Day came to a close, many were left unsatisfied with the intense focus on zero emissions vehicles and relatively no inclusion of active travel (e.g. walking and cycling).
Due to a last-minute intervention by the EU’s urban mobility coordinator Matthew Baldwin and lobbying by walking, cycling and transit organisations, however, the final declaration included a last-minute addition:
“We recognise that alongside the shift to zero emission vehicles, a sustainable future for road transport will require wider system transformation, including support for active travel, public and shared transport.”
The decision made by delegates to place little to no importance on such a critical climate solution, especially for cities, reflects an inability to think big when it comes to solving climate change.
Despite the disappointment many felt throughout COP26 as a result of weak policies, we can find hope in the younger generation. A generation of climate activists and leaders who are unwavering in their pursuit of climate justice and mission to keep 1.5 alive.
This article was guest written by Ghislaine Fandel, the Science Communication Lead & Content Director at ClimateScience. View her LinkedIn here.