Scientists finally understand why people with schizophrenia hear voices
According to new research – which represents a ‘paradigm shift’ for mental health disorders – the way people experience auditory verbal hallucinations isn’t that different from the way humans hear external sounds. For decades, scientists have been endeavouring to understand why people with schizophrenia (which affects
Current in Science
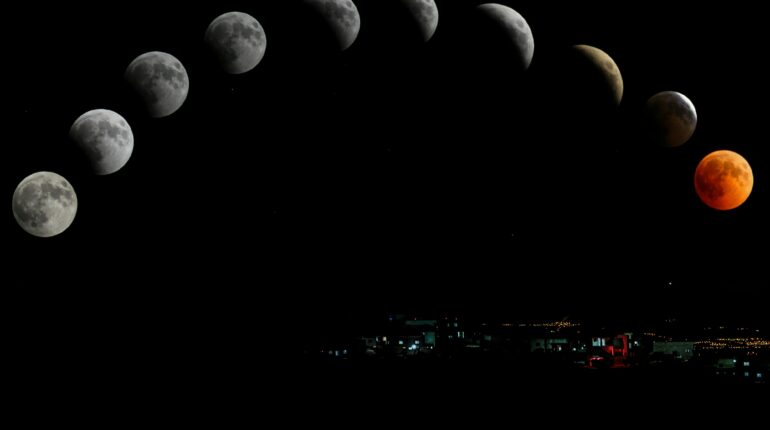
Does the moon actually influence human health?
Researchers have long dismissed such claims but surprising new evidence suggests that the lunar cycle does in fact subtly affect sleep, menstruation, and certain mental illnesses. In astrology, the moon represents the inner world – namely our emotions. Understanding how to work with its 29.5-day cycle has always been the aim...
Complex life on Earth may be 1.5 billion years older than thought
Previous studies suggest animal life did not emerge on Earth until around 635 million years ago. New research claims to have found new evidence deep within rocks showing environmental conditions for animal life 2.1 billion years ago. As it currently stands, animals first showed up on Earth around 635 million...
Immunosuppressant drug show promise of prolonging women’s fertility
Rapamycin, a drug commonly used to prevent organ transplant rejection, appears to lessen the number of egg follicles released during women’s menstrual cycles with no adverse side effects. Scientists say this could extend female fertility by up to five years. Though couples are waiting longer on average to have children,...
The ‘Internet of Animals’ is about to change our understanding of nature
A globally accessible database that documents the lives of animals and geographical structures could go live as early as next year. The collection of real-time data will inform experts on species’ behavioural changes and environmental shifts. Biologists, ecologists, and conservationists alike are concerned with the health of our planet and...
Study says the moon is slowly drifting further from Earth
Scientists say the moon is gradually moving further from Earth and that the process will eventually elongate our day cycle to 25 hours. How fast is the moon drifting? Will the Earth lose its natural satellite? Will I be forced to work overtime? So many questions. Scientists say the moon is...
Noise-cancelling headphones are good for our ears
As it turns out, while many of us are steadily destroying our hearing with unsafe listening practices, noise-cancellation might actually be our one saving grace, protecting us from the incessant din of the outside world and the neglected effects of this on our health. I wear noise-cancelling headphones every single day, often for hours at a time. As someone who’s prone to sensory overload, they’ve changed my life, making commuting to...
Why is the European Commission creating a digital twin for Earth?
A €315 million project has been launched to create a ‘digital twin’ for planet Earth. Combining Artificial Intelligence with a highly complex computer model, it aims to monitor and predict the impacts of natural phenomena and human activity on Earth. Twin… where have you been? That’s what planet Earth would be singing if it could, because it’s about to get its very first, highly accurate digital replica. Launched by The European...
Scientists theorise that the Earth may be an intelligent entity
Pointing to evidence that fungi is communicating underground to suggest that large-scale networks of life could ‘form a vast, invisible planetary intelligence,’ a group of astrobiologists are asking the thought-provoking question: if a planet like Earth can be ‘alive,’ can it also have a mind of its own? ‘Conventionally, intelligence is seen as a property of individuals. However, it is also known to be a property of collectives,’ reads the...
Study strongly evidences theory that a planet is partly buried in Earth
Ever heard the theory that the Moon was created by Earth’s collision with another planet 4.5 billion years ago? A new study has just given that belief stronger credibility. The exact origins of our Moon remain somewhat elusive, but a widely accepted theory has just received another significant boost. Unfortunately, there is no cheese involved. The hypothesis in question is officially referred to as the ‘Theia Impact Theory’ and colloquially dubbed...