Microsoft has introduced 3D telemedicine technology to increase healthcare access across rural and underserved areas in the African continent.
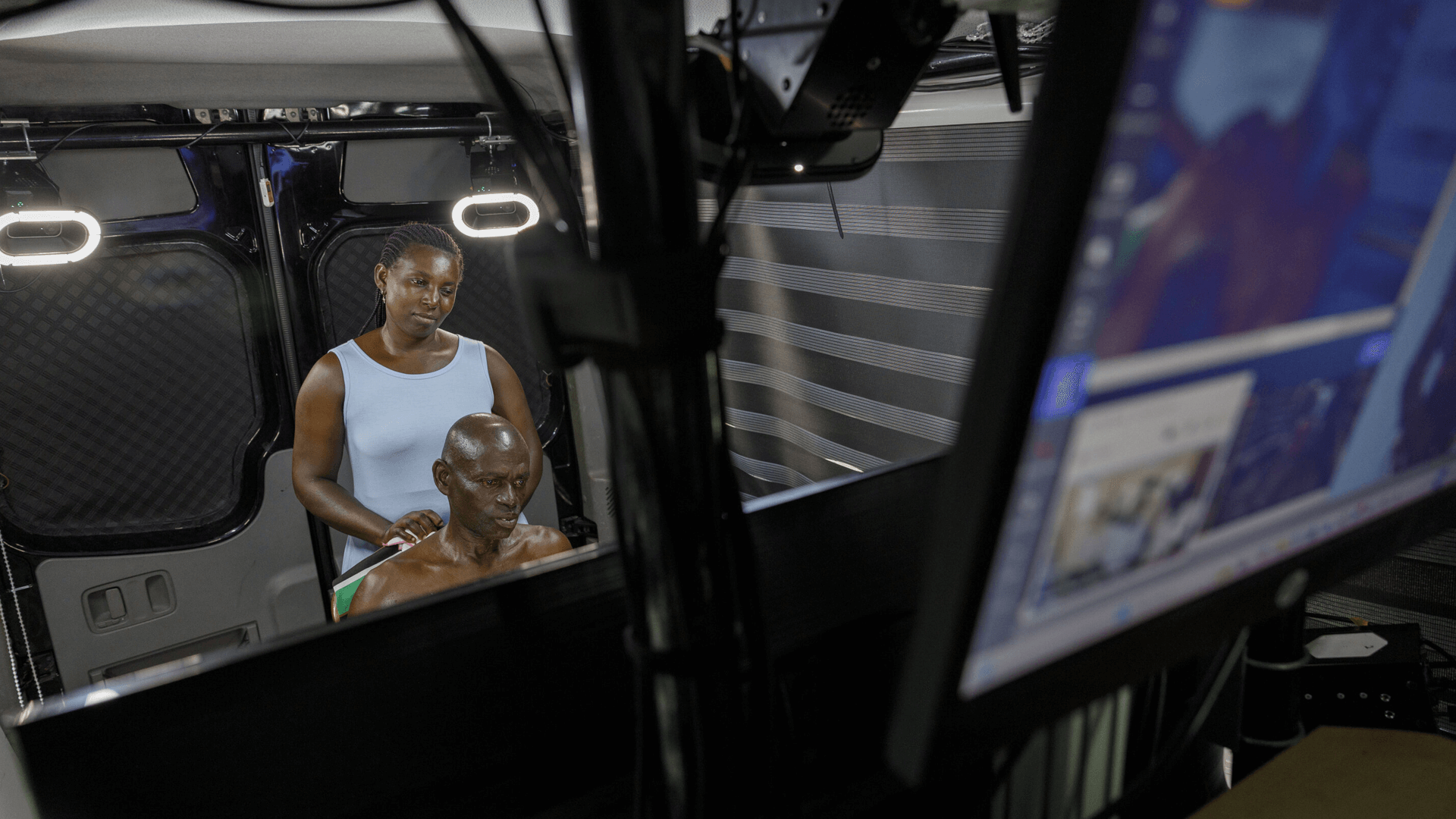
Microsoft’s 3D telemedicine service uses cutting-edge holographic and augmented reality to deliver completely immersive, real-time doctor-patient consultations.
As opposed to traditional telemedicine based on 2D video conferencing, the technology allows physicians to see patients in three dimensions for improved assessment of symptoms and conditions. The system is propelled by artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and high-speed internet connectivity.
Availability of specialized medical services in Africa has been for years hindered by poor medical facilities, limited finances and physical distance. Microsoft’s 3D telemedicine is breaking these barriers through partnerships with rural community healthcare centers. Through the partnerships, patients are now able to receive specialist consultations without the need for expensive international travel.
The 3D telemedicine is currently in rural Ghana where specialist doctors are scarce. Using this technology, patients in rural areas are now able to talk to health practitioners in Accra and even international experts. This is for the purpose of increasing early treatment and diagnosis of diseases such as cancer or heart-related illnesses.
Among the biggest obstacles to quality African healthcare is the cost of specialist care. The majority of life-saving surgeries force patients to go abroad for treatment, traveling long distances at enormous expense for those who can least afford it. Microsoft technology eliminates that expense by bringing first-class medical expertise to patients’ doorsteps.
Microsoft’s initiative is not just benefiting patients but also integrating local healthcare systems. By providing training and equipping rural health clinics with suitable digital infrastructure, the technology is empowering local health workers and physicians. Tele-mentorship and skill transfer from international experts are enhancing medical capabilities in remote areas, ultimately resulting in overall better healthcare practices.